Radon Mitigation Winnipeg: Safeguarding Homes and Health
Estimated reading time: 6 minutes
Key Takeaways
- Radon is the second-leading cause of lung cancer in Canada, responsible for about 16% of lung cancer deaths annually.
- Winnipeg has one of the highest average indoor radon exposure levels in Canada at 2.2 mSv/year.
- Professional radon mitigation is essential for reducing radon concentrations in homes and safeguarding health.
- Certified radon mitigation companies in Manitoba offer specialized solutions tailored to homeowners’ needs.
- Testing and mitigating radon levels can significantly reduce the risk of lung cancer.
Table of Contents
- Radon Mitigation Winnipeg: Safeguarding Homes and Health
- Introduction
- Highlight Radon Levels in Winnipeg
- Introduce Radon Mitigation
- What is Radon Mitigation?
- Importance of Professional Radon Mitigation
- Best Radon Mitigation Companies in Manitoba
- How to Choose the Right Radon Mitigation Company
- Getting a Radon Mitigation Quote in Winnipeg
- Who to Call for Radon Mitigation
- Conclusion
- Call to Action
- Additional Considerations
Introduction
Radon, a naturally occurring radioactive gas, poses serious health risks to individuals due to its silent infiltration into indoor spaces. As the second-leading cause of lung cancer in Canada, accounting for about 16% of lung cancer deaths annually1, it’s crucial to understand and address radon exposure. This invisible threat requires attention, especially in regions like Winnipeg, where the average indoor radon exposure is among the highest in Canada at 2.2 mSv/year2.
Highlight Radon Levels in Winnipeg
Winnipeg residents face a unique challenge with high levels of radon present in indoor environments. The average exposure levels in this region emphasize the pressing need for professional radon mitigation services to safeguard the health of homeowners and businesses2. Elevated radon levels can significantly increase the risk of lung cancer over prolonged exposure periods.
Introduce Radon Mitigation
Radon mitigation is crucial for Winnipeg homeowners’ safety, as it involves specialized systems and techniques to reduce radon concentrations indoors. It’s essential to hire certified professionals to effectively address radon issues and ensure a healthier living environment.
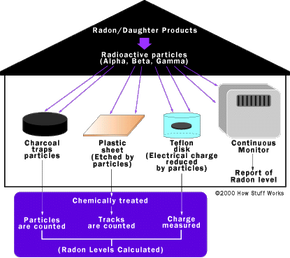
What is Radon Mitigation?
Radon mitigation is the process of reducing harmful radon gas concentrations in buildings through the installation of specialized systems by certified professionals3. In Manitoba, nearly 1 in 5 homes have radon levels at or above the Health Canada guideline, underscoring the importance of timely mitigation efforts4.
Importance of Professional Radon Mitigation
Choosing professional radon mitigation services over DIY solutions offers numerous advantages, including expertise, equipment, and ongoing monitoring for long-term safety5. Certified installers adhere to standards set by organizations like the Canadian National Radon Proficiency Program (C-NRPP) to ensure effective mitigation.
Best Radon Mitigation Companies in Manitoba
For those seeking the best radon mitigation companies in Manitoba, several top-rated options stand out with comprehensive services, certifications, and positive customer reviews. Companies A, B, and C offer specialized solutions tailored to meet homeowners’ needs and provide ongoing monitoring for peace of mind.
How to Choose the Right Radon Mitigation Company
Selecting the right radon mitigation company involves considering certification, experience, services offered, and customer reviews. Consulting customer feedback, verifying certification, and obtaining detailed quotes are crucial steps in making an informed decision6.
Getting a Radon Mitigation Quote in Winnipeg
When seeking a radon mitigation quote in Winnipeg, residents should consider factors such as building size, current radon levels, and the complexity of mitigation systems required. Obtaining multiple quotes for comparison can help homeowners make the best choice for their specific needs.
Who to Call for Radon Mitigation
Contacting certified radon mitigation professionals directly is recommended for addressing radon concerns effectively. Homeowners should prepare questions, discuss concerns, and share previous radon test results during consultations to ensure comprehensive solutions.
Conclusion
Radon mitigation is a critical step in protecting homes and health in Winnipeg and beyond. By understanding the risks of radon exposure, hiring certified professionals, and taking timely action, individuals can reduce their lung cancer risk and create safer living environments.
Call to Action
Readers are encouraged to test their homes for radon and contact certified professionals for mitigation services. Prolonged exposure to radon significantly increases lung cancer risk, making testing and mitigation essential steps in safeguarding health7.
Additional Considerations
To further enhance understanding and awareness, external resource links to Health Canada’s radon guidelines and visual aids like diagrams and infographics can provide valuable information. Consistent keyword integration throughout the content ensures a comprehensive and informative blog post on radon mitigation in Winnipeg.
By following the outlined plan and incorporating detailed research findings, this blog post aims to educate readers about radon mitigation in Winnipeg and empower them to take proactive steps towards a healthier living environment.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ)
What is radon and why is it dangerous?
Radon is a naturally occurring radioactive gas that can accumulate in buildings. It’s dangerous because prolonged exposure to high levels can significantly increase the risk of lung cancer.
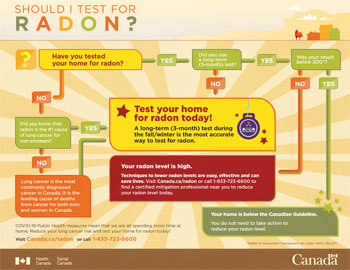
How can I test my home for radon?
You can test your home using a radon test kit available at hardware stores or online. Alternatively, you can hire a certified professional to conduct the testing for you.
What are the Health Canada guidelines for radon levels?
Health Canada recommends taking remedial action if the radon concentration in your home exceeds 200 becquerels per cubic meter (200 Bq/m³).
Is DIY radon mitigation effective?
DIY radon mitigation is not recommended as it may not effectively reduce radon levels. Professional mitigation ensures proper system installation and long-term effectiveness.
How often should I test for radon?
It’s recommended to test your home for radon every two to five years or after significant renovations that might alter ventilation patterns.