How Radon Testing Works: A Comprehensive Guide
Estimated reading time: 7 minutes
Key Takeaways
- Radon is a colorless, odorless radioactive gas that poses serious health risks, including lung cancer.
- Understanding how radon testing works is crucial for ensuring home safety.
- Various testing methods are available, including short-term and long-term tests.
- Accurate radon testing requires following proper protocols and considering influencing factors.
- Taking action based on radon testing results can protect your family from potential health risks.
Table of Contents
Introduction
Have you ever considered the unseen dangers that could be lurking in your home? One such threat is radon, a colorless, odorless radioactive gas that poses serious health risks. In this guide, we will delve into how radon testing works to ensure the safety and well-being of your household.
Radon is a leading cause of lung cancer after smoking, making it crucial to understand the importance of radon testing for your home. This comprehensive guide will walk you through the process to help you make informed decisions regarding radon exposure.
Understanding Radon
Define Radon
Radon is a colorless, odorless radioactive gas produced by the natural breakdown of uranium in soil, rock, and water. This gas can enter homes through cracks and other openings in foundations, posing a health hazard to occupants.
Health Risks
Prolonged exposure to high levels of radon significantly increases the risk of developing lung cancer, ranking as the second leading cause after smoking. It is vital to test for radon to protect yourself and your loved ones from these potential health risks.
How Radon Testing Works
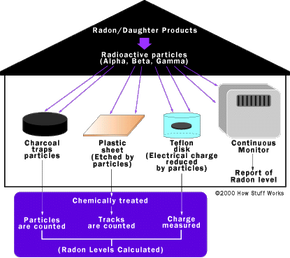
Radon testing works by detecting either radon gas directly or its radioactive decay products. Various devices, such as charcoal canisters, alpha track detectors, and electret ion detectors, are used to collect samples and measure radon levels accurately.
Different Methods of Testing
- Passive Testing: Utilizes devices like charcoal canisters and alpha track detectors that do not require power.
- Active Testing: Involves continuous radon monitors operated by professionals and powered devices for consistent monitoring.
Proper testing procedures, including correct device placement, appropriate testing duration, and following instructions accurately, are essential for accurate results.
What is a Radon Test Kit?
Definition
A radon test kit is a tool used to measure the levels of radon gas in a home or building. There are passive devices like charcoal canisters and alpha track detectors for short-term use, as well as active devices that require power and professional operation for continuous monitoring. Visit SafeRadon.ca for more information.
Factors to Consider
When choosing a radon test kit, factors like accuracy, cost, ease of use, and the need for professional assistance should be taken into account to ensure reliable results.
Short-Term vs. Long-Term Radon Testing
Difference
Short-term radon tests typically last from 2 to 90 days, providing a quick assessment. In contrast, long-term tests measure radon levels for more than 90 days to better reflect year-round exposure.
Advantages and Disadvantages
Short-term tests offer quick results but may not represent annual average radon levels accurately, while long-term tests provide a more comprehensive assessment but take longer to obtain results.
How Long Does Radon Testing Take?
Duration
Short-term testing ranges from 2 to 90 days, offering quick results, whereas long-term testing lasts over 90 days, providing a better understanding of average radon levels over time. Learn more at SafeRadon.ca Blog.
Influencing Factors
Seasonal changes, building ventilation, and usage patterns can influence radon levels, affecting the testing duration required for accurate results.
How Accurate is Radon Testing?
Accuracy
Radon testing is generally reliable when proper protocols are followed. Factors like device placement, testing duration, and home ventilation patterns can impact the accuracy of results.
Tips for Accuracy
Following manufacturer’s instructions, using EPA-recommended protocols, avoiding severe weather conditions, and placing the device in the lowest livable area of the home help ensure accurate readings.
Resources for Radon Testing
In addition to this guide, the U.S. Environmental Protection Agency (EPA) offers comprehensive resources on radon testing, mitigation, and health risks. Readers are encouraged to consult other reputable organizations and state health departments for further guidance on radon testing. Visit SafeRadon.ca for more information.
Conclusion
Understanding how radon testing works is crucial for ensuring the safety of your home and family. The risks associated with radon exposure highlight the importance of testing and taking necessary precautions. Consider testing your home for radon, explore options for purchasing a radon test kit, or hiring professionals to address any concerns.
Take action today to protect your loved ones from the potential harms of radon exposure. Remember, knowledge is power when it comes to ensuring a safe and healthy living environment.
Additional Resources/FAQs
FAQs
- How much does radon testing cost?
- How often should I test for radon?
- What should I do if high radon levels are found?
Further Reading
Explore detailed guides on radon mitigation and contact local health departments for personalized advice regarding radon testing and safety measures.
This comprehensive guide on how radon testing works provides valuable insights into the importance of radon testing, the science behind it, and the various methods available. Take charge of your home’s safety by staying informed and proactive in managing radon exposure risks. Remember, prevention is key when it comes to safeguarding your health and well-being.